Product Info from our CLT Partner
cross
laminated
timber.
Cross-laminated timber (KLH®, BSP, CLT, X-LAM, Cross-Lam) is made from spruce slats stacked atop of each other which are bonded using high press force and formaldehyde free adhesives to form large-format building elements.


The elements are statically stressed construction elements and are used as wall, ceiling and roof panels in solid timber construction projects. Thanks to the cross-wise structure of the longitudinal and cross-slats, wood expansion and shrinkage in the panel plane is reduced to an insignificant minimum. At the same time, this raises the structural load capacity and dimensional stability in the panel plane.
In accordance with the European Technical Assessment, technically dried timber with a wood humidity of 12% (+/- 2%) is used for the manufacture of KLH® solid timber boards. Destructive vermin, fungi or insect infestation is thus excluded. KLH® solid timber boards are regarded CE certified building materials. The raw slats used are sourced from sustainably forestry and are either PEFC or FSC® C119602 certified.
modern facilities.
In our modern production facilities, the elements are exclusively produced in a project-related way. The thickness of the elements and the number of plies used mostly depends on the structural and fire-protection requirements. On the basis of approved production plans, the elements are cut using state-of-the-art CNC systems. The elements are delivered directly to the construction site on a just-in-time basis, either by lorry or in a container. On location, they are mounted by the expert personnel of a timber construction company or that of a construction company using a construction crane.

Product Advantages
- Ecologically sustainable construction material
- Healthy, comfortable room climate
- Stable value with elements manageable in terms of building physics
- Highest-possible freedom in architectural implementation
- Simple planning of individual structures
- Optimal utilisation of the enclosed plot area by using slim construction elements

- Statically highly stable, large-format and thus assembly-friendly elements
- Short construction period, dry construction method and quick readiness for occupancy
- Quality-controlled production internally as well as externally
- High dimensional accuracy with CNC-controlled cut
- Technically approved and CE-marked construction product
- Delivery of the elements pre-manufactured under weather-protected conditions directly to the construction site



Solid
wood
panels.
KLH® SOLID WOOD PANELS ARE IDEALLY SUITED FOR LOAD-BEARING, BRACING AND NON-LOAD-BEARING WALL, CEILING AND ROOF ELEMENTS.


Manufacture
The crossways arrangement of the longitudinal and crosswise laminates reduces the swelling and shrinkage in the board plane to an insignificant minimum and static strength and shape retention increase considerably. According to the European Technical Assessment exclusively technically seasoned timber with a wood moisture content of 12% (+/-2%) is used. Any timber laminates are subjected to quality control before their use.

Adhesives &
lamination process
Only VOC-free and formaldehyde-free PUR adhesives are used in accordance with EN 15425. The adhesives have been tested and classified as TYPE 1 adhesives and have been approved for the production of load-bearing timber components.
The adhesive is applied automatically over the entire surface approx. 0.15 kg/m² per joint. The laminated pressure at 0.6 N/mm² used during the manufacture of KLH® solid timber panels is 6 times higher when compared with vacuum press technology. The quality of the lamination of KLH® CLT is therefore of high quality and the load-bearing capacity comparatively higher.
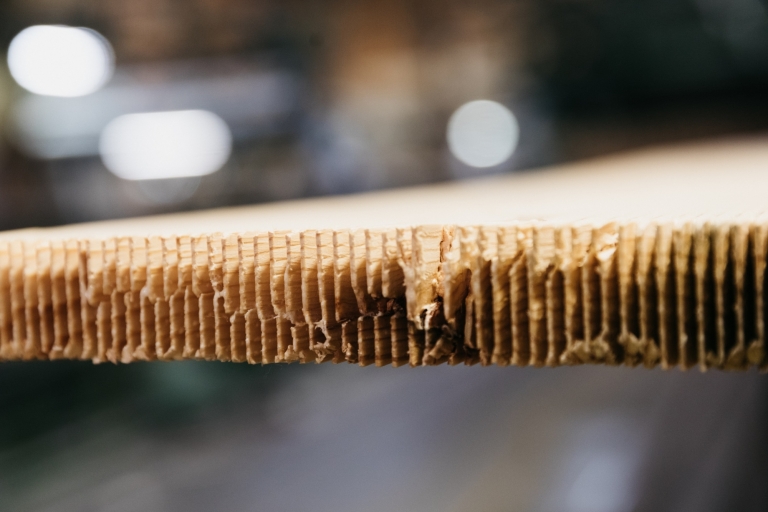

CNC – Cutting
Factory cutting or beaming takes place using state-of-the-art CNC-technology. The basis for that form the production and cutting plans released by the client or the executing company, respectively. For elements of a length and width > 1 m the tolerances are +/-2mm, for standard panel types, standard trimming and a wood moisture content of 12%.
We furthermore produce and deliver unmachined raw panels to supply CNC trimming service factories and processing mills, from where the elements are then transported to the site.
For further information please contact us.
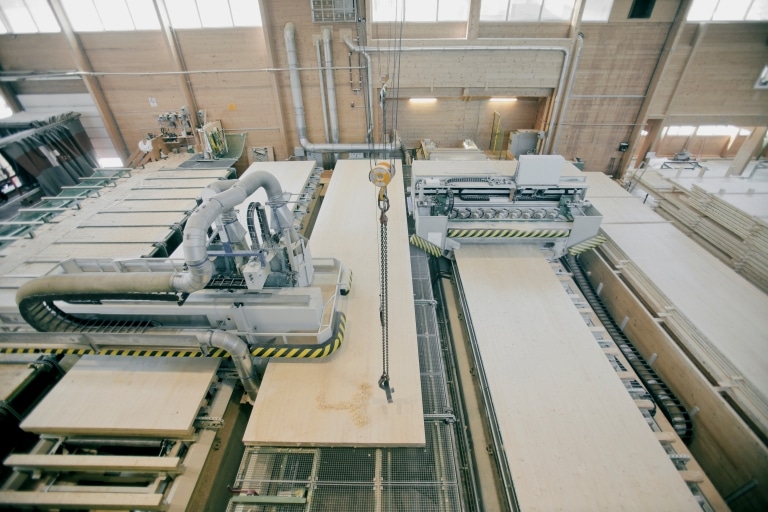
Assembly &
Installation
We are offering various lifting systems, depending on the panel type, panel size and surface quality. All lifting systems installed in our factory are CE-marked.

Technical Approvals, Certificates and Eco-labels
Panel types
KLH® solid timber panels are offered in 3 standard qualities. Upon request special surfaces and panel built-ups are possible, depending on the availability of the raw lamellas and technical feasibility. Special structures are possible upon request.
| Product name / Brand | KLH® |
| OTHER PRODUCT NAMES | Cross-laminated timber (CLT) | X-Lam |
| APPLICATION | Structural elements for walls, floors and roofs |
| DURABILITY | Service classes 1 and 2 according to EN 1995-1-1 |
| WOOD SPECIES | Spruce (pine, fir, stone pine and other wood types on request) |
| PANEL BUILD UP | 3, 5, 7 or more layers depending on static requirements |
| LAMELLAE | Thickness 20 to 45 mm, technically dried, quality-sorted and finger-jointed |
| STRENGTH CLASS | C 24 according to EN 338, maximum 10% C 16 permitted (compare ETA-06/0138) |
| ADHESIVE | Formaldehyde-free PUR adhesive, approved for load-bearing and non-load-bearing components indoors and outdoors according to EN 15425 |
| LAMINATING PRESSURE | At least 0.6 N/mm² |
| WOOD MOISTURE CONTENT | 12% (+/- 2%) on delivery |
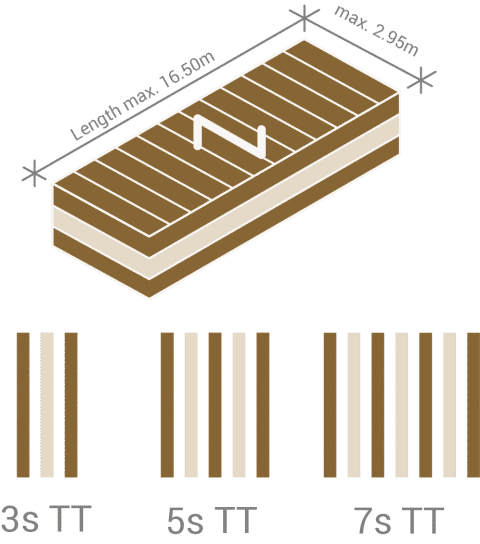
| MAXIMUM ELEMENT DIMENSIONS | Length 16.50 m / width 2.95 m / thickness 0.50 m |
| PRODUCED WIDTHS | 2.40 / 2.50 / 2.73 / 2.95 m |
| SURFACE QUALITY | Non-visual quality (NVQ) | Industrial visual quality (IVQ) | Domestic visual quality (DVQ) Special surfaces on request |
| WEIGHT | 5.5 kN/m³ according to ÖNORM B 1991-1-1:2011 for structural analysis 500 kg/m³ for determination of transport weight |
| MOISTURE MOVEMENT | In panel plane 0.01% per % change in wood moisture content, perpendicular to panel plane (panel thickness direction) 0.24% per % change in wood moisture content |
| THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY | λ = 0.12 W/(m*K) according to EN ISO 10456 |
| HEAT STORAGE CAPACITY | cp = 1600 J/(kg*K) according to EN ISO 10456 |
| VAPOUR RESISTANCE | µ = 20 to 50 according to EN ISO 10456 |
| AIR TIGHTNESS | KLH® solid wood panels can generally be used as airtight layers. Connections to other components, butt joints, penetrations, etc. must be sealed appropriately. |
| REACTION TO FIRE | Euro class D-s2, d0 |
| RESISTANCE TO FIRE | According to ETA – 06/0138 |
By using double layers, the board’s longitudinal and transverse rigidity can be increased in a targeted manner. Changes to the board structure can be used to increase its fire resistance in order to meet special project requirements.

Panel types
Overview
| Nominal thickness in mm | in Layers | Typ | Lamella structure [mm] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | L | C | L | C | L | C | ||||
| KLH® | 60mm | 3s | TT | 20 | 20 | 20 | ||||
| KLH® | 70mm | 3s | TT | 20 | 30 | 20 | ||||
| KLH® | 80mm | 3s | TT | 30 | 20 | 30 | ||||
| KLH® | 90mm | 3s | TT | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||||
| KLH® | 100mm | 3s | TT | 30 | 40 | 30 | ||||
| KLH® | 110mm | 3s | TT | 40 | 30 | 40 | ||||
| KLH® | 120mm | 3s | TT | 40 | 40 | 40 | ||||
| KLH® | 100mm | 5s | TT | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | ||
| KLH® | 110mm | 5s | TT | 20 | 20 | 30 | 20 | 20 | ||
| KLH® | 120mm | 5s | TT | 30 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 30 | ||
| KLH® | 130mm | 5s | TT | 30 | 20 | 30 | 20 | 30 | ||
| KLH® | 140mm | 5s | TT | 30 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 30 | ||
| KLH® | 150mm | 5s | TT | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||
| KLH® | 160mm | 5s | TT | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | ||
Fire Protection
Crosslam timber / CLT- Fire resistance and rating
One of the major advantages of Cross Laminated Timber is its inherent fire resistance. CLT can be designed to accommodate substantial fire resistance and unlike steel remains structurally stable when subjected to high temperatures. CLT panels can be produced with fire resistances of 30, 60 and 90 minutes.
It’s easy to see why any form of timber construction can pick-up a reputation for fire risk, but for solid wood and Cross Laminated Timber, performance in a fire is a long way from their timber frame cousins.
To understand how efficient CLT is in a fire, we should start with the understanding that fire resistance is the ability of a material to confine a fire or to continue to provide a structural function or both.
The measure of fire resistance is the time elapsed from the start of the fire up until the point where the material fails to function. Typically resistance is expressed in minutes eg FR 30, 45, 60 or 120.
CLT’s fire resistance is provided through ‘charring’. As the face of the timber panel is exposed to a fire that ramps up to a temperature in excess of 400 degrees C, the surface of the timber ignites and burns at a steady rate. As the timber burns it loses its strength and becomes a black layer of ‘char’. The char becomes an insulating layer preventing an excessive rise in temperature within the unburnt core of the panel. It is this unaffected core which continues to function for the period of the fire resistance.
To achieve the designed fire resistance period there must be sufficient virgin solid timber remaining behind the char layer to sustain the loads applied. Therefore each CLT panel within the building must be designed for the fire resistance period and the specific loadings applied to that panel.
Fire resistance testing of CLT panels is to ISO 834 – the same standard used for doorsets which most of us are familiar with.
Illustration showing a typical temperature / time gradient through solid timber under fire conditions
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRIPQ_q2iyY







